Les outils du logiciel libre pour l’ingénieur
CentraleSupélec
2025-11-30
Syllabus
Contenu du cours
Philosophie du cours
Vous introduire au monde du logiciel libre (free software) avec sa dimension philosophique et pratique.
Au programme
- 1 CM (1h30) : introduction au logiciel libre et à GNU/Linux
- 1 TP (4h) d’introduction au shell Bash et à Git,
- 1 TP (4h) visant à produire une vidéo d’une éruption solaire,
- 1 TP (4h) visant à produire une animation des températures aux États-Unis
Ressources
Plusieurs outils sont illustrés par la pratique et triés par besoin sur https://jeremyfix.github.io/OutilsLibres/
Vous pouvez suggérer des modifications sur le dépôt GIT https://github.com/jeremyfix/OutilsLibres
Le pôle logiciel libre de la DINUM administre le Socle Interministériel du Logiciel Libre (SILL)
Évaluation
- pas de contrôle terminal
- évaluation par les rendus de TP (rapport en LaTeX, code sur GIT !!)
Introduction au logiciel libre
Logiciel libre \(\neq\) open source
Philosophie libre
Les quatre libertés selon la Free Software Foundation :
- la liberté de faire fonctionner le programme comme vous voulez, pour n’importe quel usage (liberté 0) ;
- la liberté d’étudier le fonctionnement du programme, et de le modifier pour qu’il effectue vos tâches informatiques comme vous le souhaitez (liberté 1)
- la liberté de redistribuer des copies, donc d’aider les autres (liberté 2) ;
- la liberté de distribuer aux autres des copies de vos versions modifiées (liberté 3) ; en faisant cela, vous donnez à toute la communauté la possibilité de profiter de vos changements.
L’accès au code source (open source) est une condition nécessaire mais pas suffisante pour les libertés 1 et 2.
Exemples
- Kernel Linux, code source, Licences
- GIT, code source, Licence GNU GPL v2
- GCC, code source, Licence GNU GPL v3
- Python, code source de l’interpréteur CPython, Licence Python Software Foundation License V2
- Firefox, code source, Licence Mozilla Public License v2
- GIMP, code source, Licence GNU GPL v3
Les licences
Un grand nombre de licences existent, même parmi celles qui respectent les 3 libertés (utilisation, modification, partage) : https://opensource.org/licenses.
Licence GPLv3 : licence à fort copyleft (non permissive / contaminante / avec obligation de réciprocité) en droit anglo-saxon / Licence CeCILL en droit français
Licence BSD : licence permissive (elle permet d’en dériver un logiciel propriétaire)
Licences Creative Commons CC : Creative commons chooser
Logiciel libre \(\neq\) gratuit
Free software \(\neq\) free beer.
Il est tout à fait envisageable de développer des modèles économiques autour du logiciel libre :
- Red Hat Enterprise (env. \(200 \$\) pour une station) vs Fedora : Fedora and Red Hat Enterprise
- Moodle met à disposition son code source et permet, contre rétribution, à des partenaires (e.g. edunao) de vendre une solution basée sur moodle.
- des communautés se forment pour le développement de ces logiciels
Distributions Linux
Une distribution Linux =
- système d’exploitation basé sur le noyau Linux
- un gestionnaire de paquets (e.g. apt, yum, dnf, brew, …)
- un logiciel de démarrage
init(e.g. sysv, systemd, launchd, …) - les outils GNU
- le programme getty qui offre des terminaux sur les F2, F3, etc.
- éventuellement un serveur graphique (e.g. Xorg, Wayland) et un gestionnaire de bureau (e.g. Gnome, KDE, XFCE, etc.)
Il existe beaucoup de distributions (voir https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Linux_distribution#/media/File:Linux_Distribution_Timeline.svg), en général dérivées de :
- Slackware
- Debian (Ubuntu, etc.)
- Red Hat (Fedora, etc.)
- Arch
- Gentoo
- SUSE
GNU/Linux
Philosophie Unix
Unix est le noyau (+outils) commercial développé par AT&T labs. Linux est développé par Linus Torvalds dans les années 1990.
Do one thing and do it well - Doug McIlroy
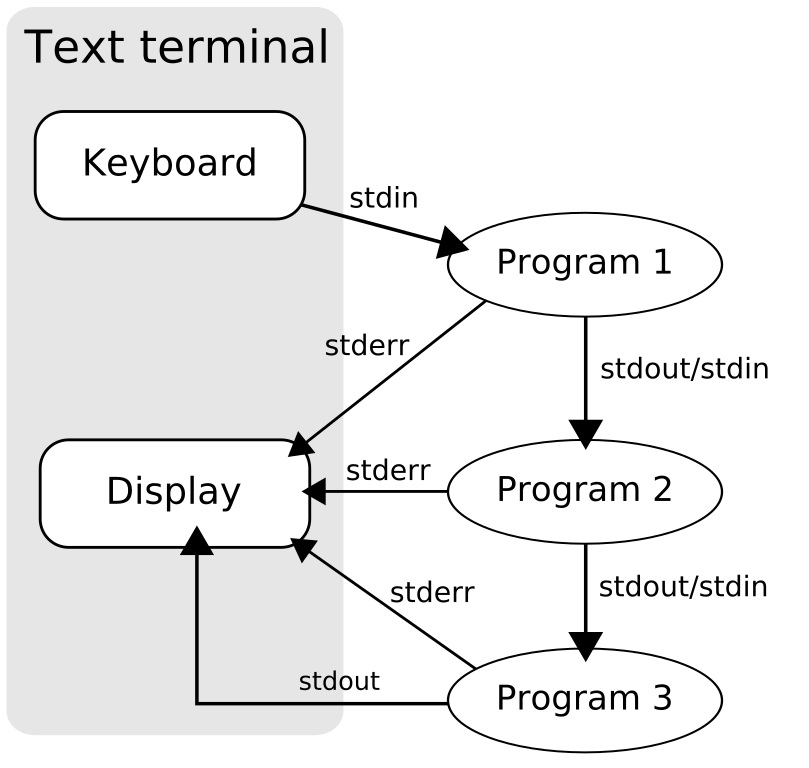
On dispose de plusieurs “petits” outils combinables. D. McIlroy a inventé le concept de “filters/pipes”, au sein d’un shell, e.g. Bourne-Again shell (bash)
Avec GNU Bash, on peut piper “|” des commandes, ou rediriger les entrées et les sorties
Organisation du système de fichiers
Plus d’infos :
ou sur la spécification Filesystem Hierarchy Standard
Extrait :
NAME
hier - description of the filesystem hierarchy
DESCRIPTION
A typical Linux system has, among others, the following directories:
/ This is the root directory. This is where the whole tree starts.
/dev Special or device files, which refer to physical devices. See mknod(1).
/etc Contains configuration files which are local to the machine. Some larger software packages, like X11, can have their own subdirectories below /etc
/home On machines with home directories for users, these are usually beneath this directory, directly or not.
/media This directory contains mount points for removable media such as CD and DVD disks or USB sticks.
/mnt This directory is a mount point for a temporarily mounted filesystem.
/opt This directory should contain add-on packages that contain static files.
/proc This is a mount point for the proc filesystem, which provides information about running processes and the kernel. This pseudo-filesystem is described in more detail in proc(5).
/root This directory is usually the home directory for the root user (optional).
/tmp This directory contains temporary files which may be deleted with no notice, such as by a regular job or at system boot up.
/usr This directory is usually mounted from a separate partition. It should hold only shareable, read-only data, so that it can be mounted by various machines running Linux.
/usr/bin This is the primary directory for executable programs. Most programs executed by normal users which are not needed for booting or for repairing the system and which are not installed locally should be placed in this directory.
/usr/include Include files for the C compiler.
/usr/lib Object libraries, including dynamic libraries, plus some executables which usually are not invoked directly.
/var This directory contains files which may change in size, such as spool and log files.
! Utilisez l’auto-complétion pour naviguer
Permissions
Utilisateurs
- L’utilisateur spécial
roota tous les droits (super-utilisateur) - Les utilisateurs appartiennent à des groupes
id - Un utilisateur peut être autorisé à passer super-utilisateur (groupe sudoers)
Permissions
Les permissions données à un groupe dépendent de flags. Ces permissions sont de trois types, notées “rwx” pour r-ead, w-rite, e-x-ecute :
- permission de lire un fichier ou lister le contenu d’un répertoire
- permission d’écrire (modifier) un fichier, ou de créer, supprimer, déplacer des éléments d’un répertoire
- permission d’exécuter un fichier et d’accéder au contenu d’un répertoire.
Et il y a 3 groupes de permissions :
- le propriétaire du fichier/répertoire
- les membres du groupe propriétaire du fichier/répertoire
- le reste du monde
Autre exemple :
- Changement des permissions par
chmod. Changement de propriétaire parchown
Voir aussi https://debian-handbook.info/browse/stable/sect.rights-management.html
Outils de base
Illustrations des outils de base
Utilisation du shell, Utiliser l’historique des commandes
Installer de nouveaux packages
Compresser/décompresser
Editer du texte/du code : vim, emacs, code
Ecrire un rapport/une présentation en LaTeX ou Markdown
Versionner du code : git, github, gitlab. Voir Visual git reference et tutoriels
Obtenir de l’aide
Obtenir de l’aide
Illustration de :
- man
- tldr
- info
La documentation de la distribution Ubuntu, Debian, Arch
Le wiki Ubuntu-fr : https://doc.ubuntu-fr.org/
Utilisation du shell
Kit de survie
- Au fait, pourquoi utiliser le shell ? C’est un truc de geek ? Vraiment ?
Naviguer dans le système de fichier :
cd,lsCréer un répertoire
mkdir, Supprimer un répertoirerm -rInspecter le contenu d’un fichier
lessObtenir le début
head, la fintailConnaître la taille d’un fichier / répertoire :
duLister les espaces disques
dfinteragir avec l’historique
history,Ctrl+R
Vous pouvez personnaliser vos shells avec des rc-files
Installer de nouveau packages
Installer de nouveaux packages
Une distribution Linux vient avec un gestionnaire de paquets : dnf, apt, pacman, etc.
Sous Ubuntu, par exemple pour installer Texlive :
Ubuntu utilise aussi d’autres formats, e.g. snap (conteneurisé), appimage (installable dans l’espace utilisateur), etc.
https://jeremyfix.github.io/OutilsLibres/outils/familiarisation/#installations-logicielles
Compresser / décompresser
Compresser / décompresser
Il existe plusieurs formats d’archives : zip, 7z, tar, tar.gz, etc.
$ tldr 7z
7z
File archiver with a high compression ratio.
More information: https://manned.org/7z.
...
- Encrypt an existing archive (including filenames):
7z a path/to/encrypted.7z -ppassword -mhe=on path/to/archive.7z
...
- E[x]tract an archive to a specific directory:
7z x path/to/archive.7z -opath/to/output$ tldr tar
tar
Archiving utility.
Often combined with a compression method, such as gzip or bzip2.
More information: https://www.gnu.org/software/tar/manual/tar.html.
...
- [c]reate a g[z]ipped archive and write it to a [f]ile:
tar czf path/to/target.tar.gz path/to/file1 path/to/file2 ...
...
- E[x]tract a (compressed) archive [f]ile into the current directory [v]erbosely:
tar xvf path/to/source.tar[.gz|.bz2|.xz]
...Editer du texte/du code
Éditer du texte/du code
Recommandation :
- VS Code par défaut
- ou sinon des outils comme Emacs, vim, nvim, etc. pour les utilisateurs plus avancés
Filtrer et manipuler du texte
Recherche de fichier ou de contenu
On peut rechercher un fichier avec find ou locate :
On peut utiliser le | sur la sortie, e.g. pour compter le nombre de fichier python dans le répertoire courant :
On peut exécuter des commandes sur les fichiers trouvés, e.g. trouver les occurrences de import numpy dans les fichiers Python
Pour trouver du contenu dans un fichier, on peut utiliser grep ou rg (ripgrep)
$ tldr grep
Find patterns in files using regexes.
More information: https://www.gnu.org/software/grep/manual/grep.html.
- Search for a pattern within a file:
grep "search_pattern" path/to/file
- Search for a pattern in all files recursively in a directory, showing line numbers of matches, ignoring binary files:
grep [-rnI|--recursive --line-number --binary-files=without-match] "search_pattern" path/to/directoryFiltrer et manipuler du texte
On peut rechercher/manipuler du contenu de fichier avec awk :
- Afficher la première colonne (Attention aux ” vs ’)
- Afficher la troisième colonne en précisant le séparateur
- Afficher la troisième colonne si la deuxième colonne a une valeur plus petite que 10
Il est possible de préciser le séparateur de sortie -OFS. Plus d’exemples en TP !
On peut également utiliser sed pour opérer des substitutions :
- Substituer une chaîne de caractères (
-ien place) :
- Insérer un copyright en tête de tous les fichiers sources C++ (cf
info sed)
On peut aussi utiliser des classes de caractères
Manipuler/Annoter/Rédiger un rapport
Manipuler/Annoter des documents PDF
On peut :
- manipuler les pages d’un pdf avec
pdftk - directement annoter/signer un PDF avec xournal++ (ou directement dans thunderbird)
$ tldr pdftk
pdftk
PDF toolkit.
More information: https://www.pdflabs.com/docs/pdftk-man-page/.
- Extract pages 1-3, 5 and 6-10 from a PDF file and save them as another one:
pdftk input.pdf cat 1-3 5 6-10 output output.pdf
- Merge (concatenate) a list of PDF files and save the result as another one:
pdftk file1.pdf file2.pdf ... cat output output.pdf
...Écrire un rapport en LaTeX
Les outils de base peuvent être :
- un IDE (e.g. VSCode) pour écrire le rapport en LaTeX associé à un moteur de compilation (e.g. TexLive), un moteur de production (e.g. Makefile, latexmk)
Templates LaTeX : https://latextemplates.com/
Un document LaTeX va gérer :
- la mise en page
- la compilation d’images (e.g. TikZ)
- les références croisées
\label{sec:masection} ... \ref{sec:masection} - les références bibliographiques au format BibTeX
\cite{Euler1748}
Écrire un rapport en Markdown
Les outils de base peuvent être :
- un IDE (e.g. VSCode) pour écrire le rapport en markdown associé à un moteur de compilation (e.g. quarto)
# Introduction
## L'origine du monde {#sec-origine}
L'origine du monde est une œuvre peinte par Gustave Courbet, exposée au musée d'Orsay depuis 1995. Cette œuvre est représentée sur la figure @fig-origine.
{#fig-origine}
## Un peu de python ?
```{python}
#| label: fig-line-plot
#| fig-cap: "A line plot "
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plt.plot([1,23,2,4])
plt.show()
```Exemples Quarto : https://quarto.org/docs/gallery/
Un document Markdown/Quarto va gérer :
- la mise en page
- la compilation d’images (e.g. TikZ, Python, R)
- les références croisées
#sec-origine, #fig-xxx ... @sec-origine, @fig-xxx - les références bibliographiques au format BibTeX
[@Euler1748]
Voir par exemple le Tutorial Quarto / VS Code
Réaliser une présentation
Produire des transparents en markdown
On peut “coder des slides” (plutôt que du drag/drop clique bouton) en utilisant Quarto/Markdown
---
title: "Les outils du logiciel libre pour l'ingénieur"
author: "Jérémy Fix"
institute: "CentraleSupélec"
date: last-modified
---
# Syllabus
## Contenu du cours
::: {.callout-note}
### Philosophie du cours
Vous introduire au monde du logiciel libre (*free software*) avec sa dimension philosophique et
pratique.
[Free software $\neq$ free beer](https://www.gnu.org/philosophy/selling.html).
:::
...Les supports peuvent être générés en HTML (dynamique), PDF (statique).
Voir par exemple les slides de ce cours
Manipuler des images, des vidéos
Manipuler des images, des vidéos
On peut éditer des images/vidéos avec :
- imagemagick et ses outils
convertoumogrifypour le traitement par lot - des outils graphiques comme gimp, inkscape, etc. et produire des images vectorielles (e.g. pdf, svg)
- des langages de programmation, e.g. TikZ intégrable dans vos documents LaTeX/Markdown

- ffmpeg / avconv pour les vidéos
https://jeremyfix.github.io/OutilsLibres/outils/images/, https://jeremyfix.github.io/OutilsLibres/outils/vectoriel/
Interagir avec une machine distante
Interagir avec une machine distante
On peut accéder à des machines distantes pour :
- accéder à des fichiers, e.g.
scp,rsync,sshfs,mount - y éditer du code, lancer du code, e.g.
ssh - accéder à un bureau graphique, e.g.
vnc - conserver une session active sur une machine distante avec
screen,byobu
Pour se connecter sur ces plateformes, différents systèmes d’authentification existent :
- basé sur un mot de passe
- basé sur une clé SSH (chiffrement symétrique)
Produire un site web
Produire un site web
Différents outils permettent de produire des sites web :
- statiques, e.g. hugo (Apache 2.0), mkdocs (BSD-2) et mkdocs-materials (MIT)
- dynamiques, e.g. django (BSD-3)
Les sites web statiques peuvent être générés et livrés par de l’intégration continue sur la plateforme qui héberge votre dépôt Git !
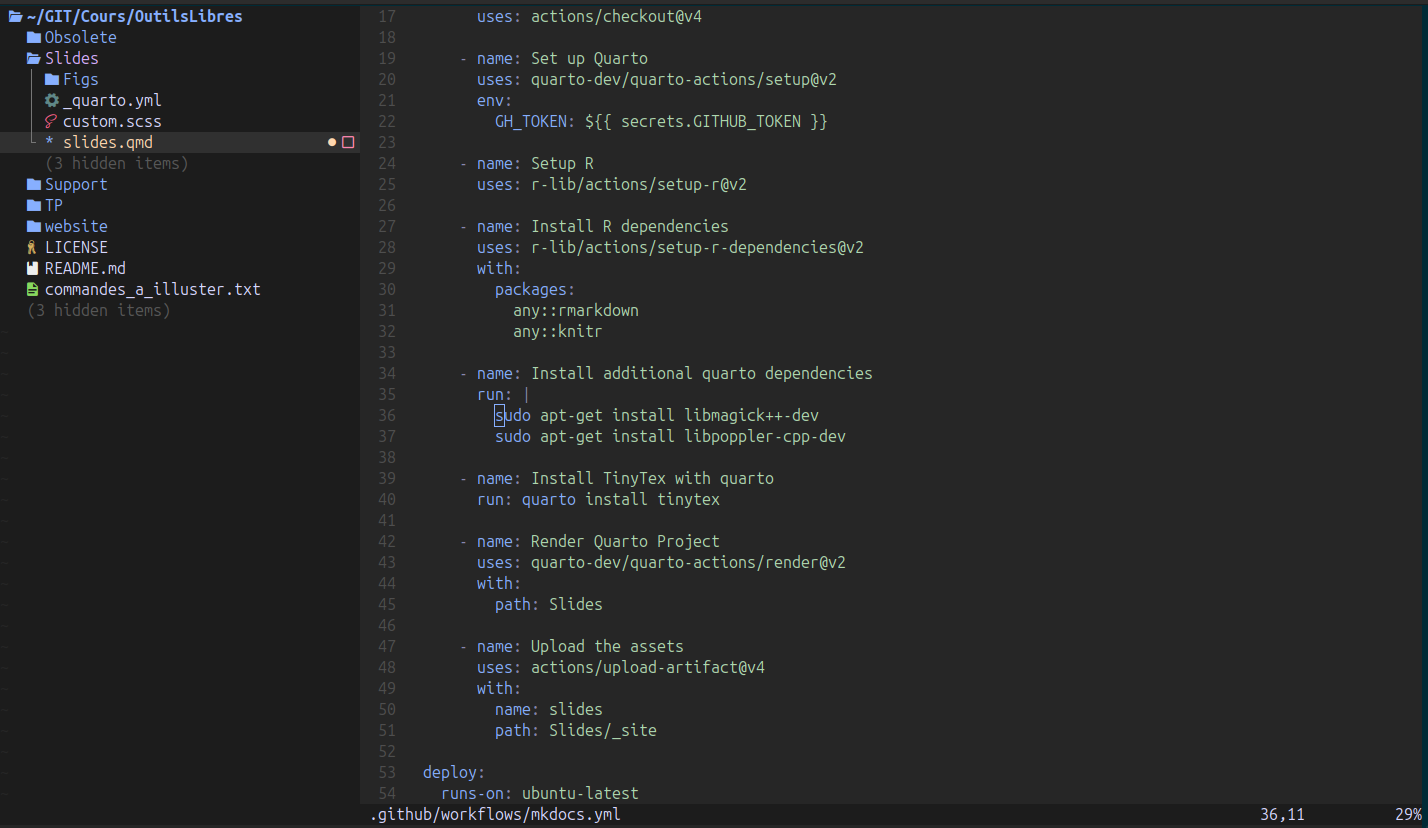
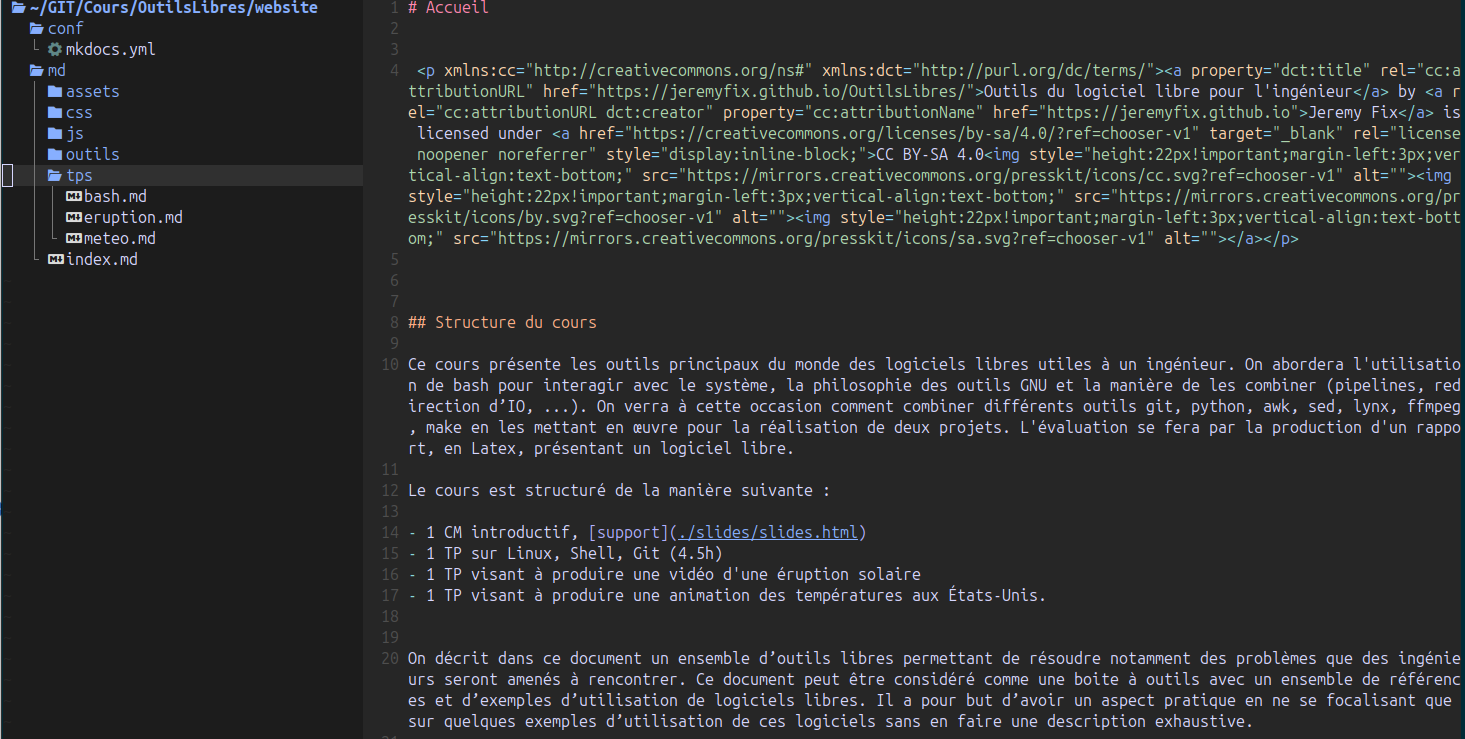
Le site du cours https://jeremyfix.github.io/OutilsLibres/ est produit avec mkdocs, voir les sources, voir Figure 1.
Automatiser des tâches
Introduction
La production d’un fichier peut dépendre d’autres fichiers qui peuvent dépendre… e.g. un rapport LaTeX -> PDF qui nécessite des illustrations
La production d’une dépendance peut nécessiter l’exécution d’un programme, e.g. une illustration PDF produite à partir d’un fichier source Ipe
Un moteur de production permet “d’automatiser l’ensemble des actions contribuant, à partir de données sources, à la production d’un ensemble logiciel opérationnel” :
- assez général : make, rake, scons, waf
- spécifique Qt/C++ : qmake
- spécifique Java : ant, maven
- utilisables pour plusieurs langages : gradle
Exemple : compiler des sources C++
Exemple de Makefile pour compiler un projet C++, illustrant les variables automatiques
TARGET=app
SRCS=$(wildcard src/*.cpp)
OBJS=$(patsubst %.cpp,%.o, $(SRCS))
# Default target
all: $(TARGET)
# Links the executable
$(TARGET): $(OBJS)
g++ -o $@ $^
# Build the object files from the sources
%.o: %.cpp
$(CXX) $(CXXFLAGS) -c $< -o $@
# Clean up the project tree
clean:
rm -f $(OBJS) $(TARGET)
# Phony targets are executed even if files called "clean" or "all" exist
.PHONY: clean allExemple : compiler un rapport LaTeX
Exemple de Makefile utilisé pour générer le support de cours Architecture des ordinateurs
IPE_SOURCES=$(wildcard Figs/*.ipe)
IPE_PDF=$(patsubst %.ipe,%.pdf,$(IPE_SOURCES))
SOURCES=$(wildcard *.tex)
support.pdf: $(SOURCES) ipe_pdf
latexmk -pdf support.tex
clean:
rm -f *~ *.aux *.log
ipe_pdf:$(IPE_PDF)
@echo "ipe to pdf conversion done"
Figs/%.pdf: Figs/%.ipe
@ipetoipe -pdf $^ 2> /dev/null
@echo "$@ generated"
ascii_table.pdf:ascii_pdf.tex
latexmk -pdf ascii_pdf.tex
pdfcrop ascii_pdf.pdf
pdftk A=ascii_pdf-crop.pdf cat A2 output ascii_table.pdf
.PHONY: clean ipe_pdfVersionner du code : une introduction au vocabulaire GIT
Mais pourquoi ?
Un code versionné permet :
- le travail collaboratif sur la “même base de code” : développement parallèle avec des branches
- de garder un historique des modifications
- de revenir en arrière sur des modifications ou conserver différentes versions simultanément
Un code peut être versionné :
- sur des plateformes privées comme https://www.github.com
- sur des plateformes auto-hébergées comme gitlab - e.g. https://gitlab-student.centralesupelec.fr
- en local : git bare repository
Plusieurs systèmes de versionnement existent (e.g. svn, mercurial, git)
Les à-côtés
Des plateformes comme GitHub / GitLab offrent plus que du versionnement :
intégration et déploiement continu CI/CD pour :
- lancer des tests unitaires
- générer et rendre accessible la documentation d’un projet
- livrer une librairie, e.g. Python sur PyPI
recueillir des
issueshistoriser les fusions
mergevia des merge requestsorganiser les tâches dans des tableaux de bord
héberger un site web (GitLab pages), des images Docker, etc.
Votre projet Git peut être local, ou synchronisé avec un serveur remote (e.g. GitHub, GitLab auto-hébergé, etc.).
Si synchronisé avec un serveur distant : git push, git pull
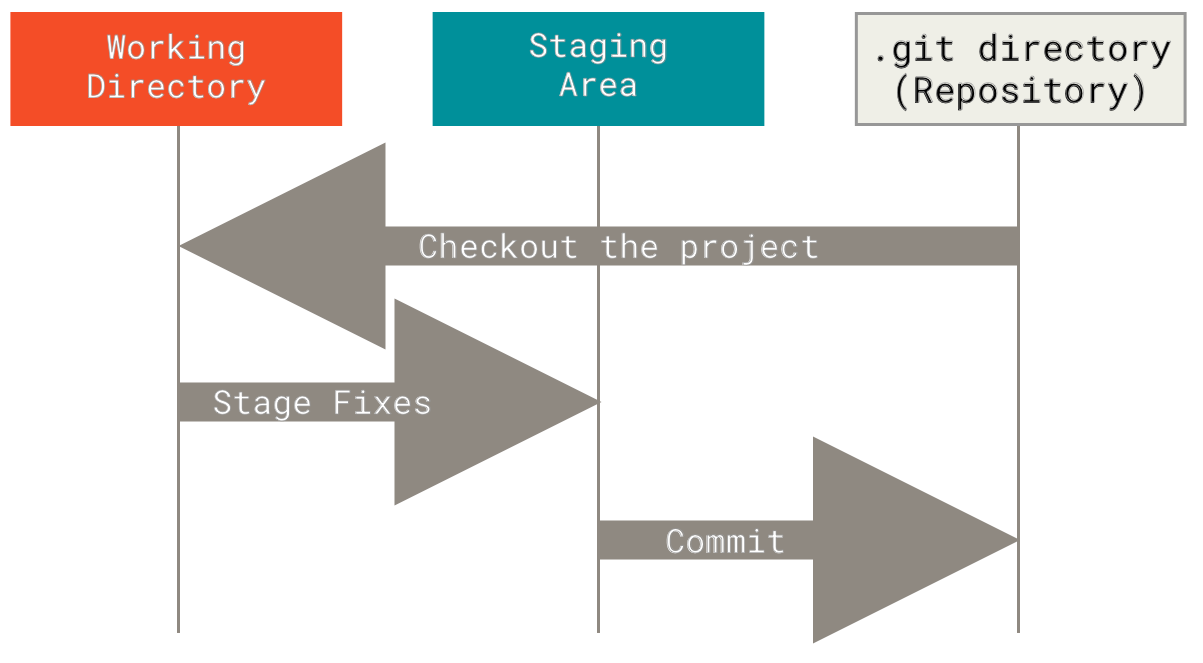
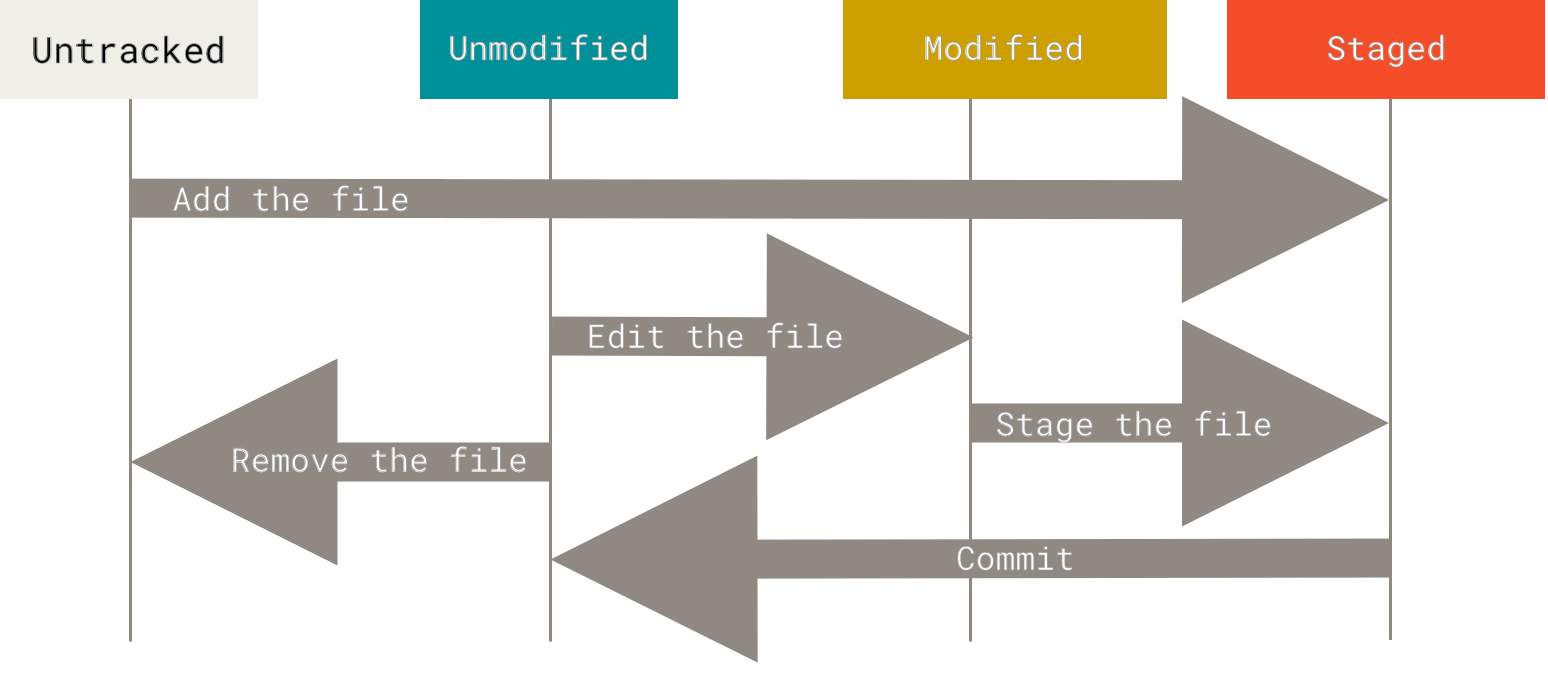
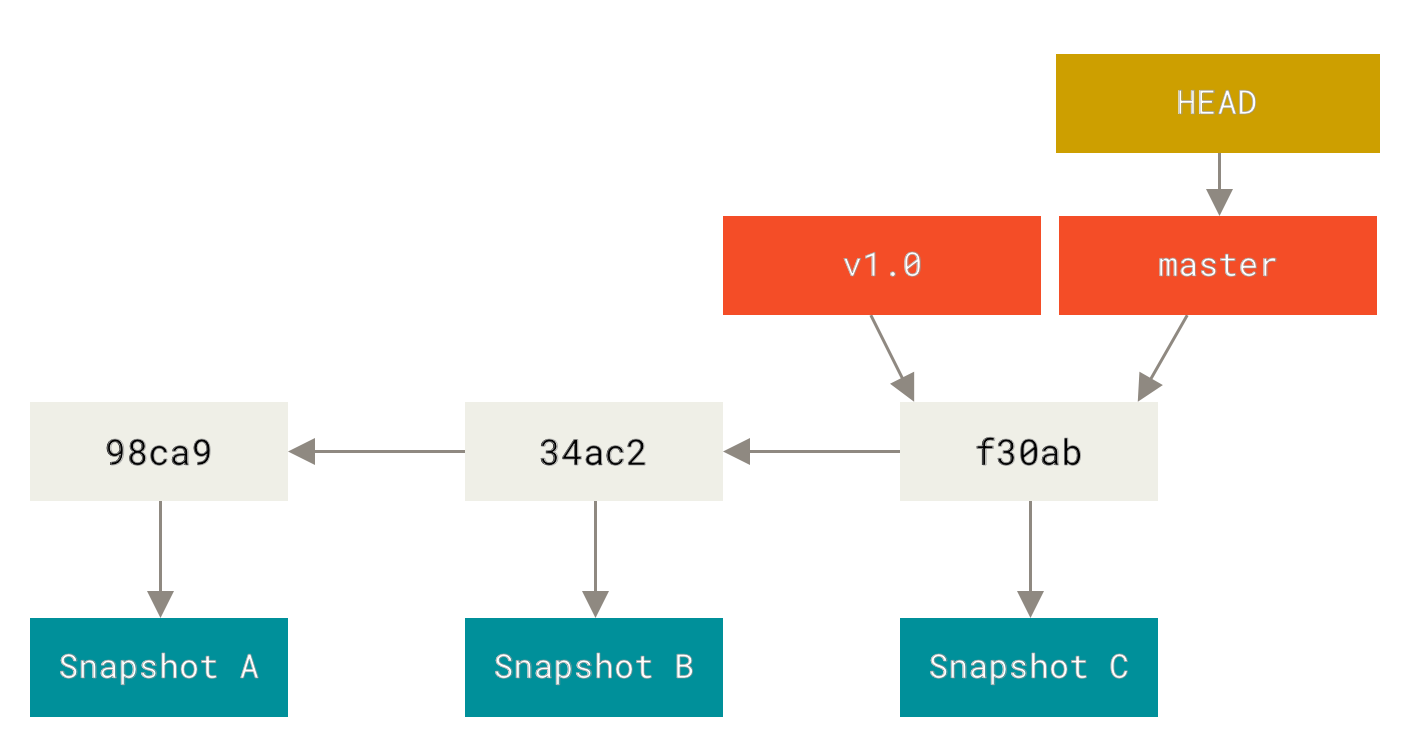
Les statuts d’un fichier dans un dépôt Git
Git prend des instantanés snapshots de votre répertoire, appelés commit associés à un commit-id.
De Pro Git :
Branches
Pourquoi les branches :
- pour le travail collaboratif et développer une fonctionnalité “dans son coin”
- pour développer une fonctionnalité sans impacter une version “stable”, en production
- pour tester une idée sans impacter une version “stable”, en production
Les branches sont des étiquettes dans l’arbre des commits.
Commandes utiles : git branch -a, git checkout -b <branch_name>, git checkout <branch_name>
Fusion
Merge (request) :
- une fois la fonctionnalité finalisée
- ajout sur la branche principale (
mainoumasteren général)
Le merge peut être soumis à relecture Pull Request (PR)
⚠ Vous pouvez être confronté à des conflits :
- Git balise les conflits
- il vous revient de résoudre le conflit puis de committer la résolution
Fin
Merci pour votre attention
La suite en TP !

Produced with quarto